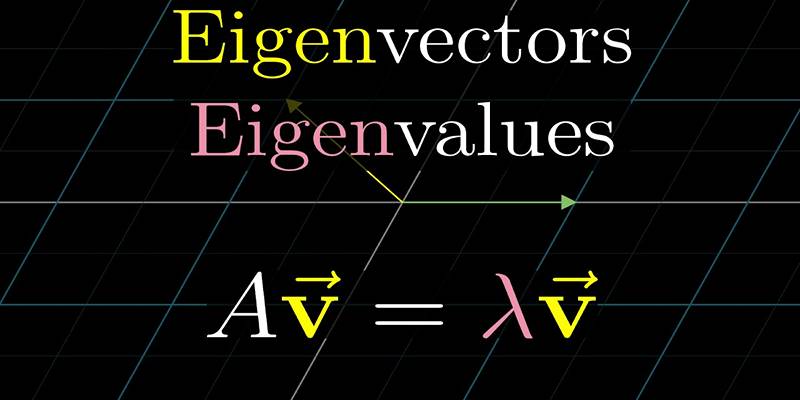As AI development becomes more widespread, there's increasing interest in how large language models (LLMs) are shared with the world. Some models are completely locked down, while others are openly released in some way. But terms like “open weight models” and “open source models” are often used without clarity.
With the release of DeepSeek models, a Chinese AI lab has fully embraced the open-weight approach. Likewise, Google’s Gemma 3 and a soon-to-be-released OpenAI open-weight model reflect a growing shift toward open AI. But what does this really mean? This guide breaks down key concepts like model weights, explains the differences between open-weight and open-source models, and outlines how each impacts AI practitioners.
What are Weights in LLMs?
At the core of every AI model lies something called weights. These are numerical values learned during training. Think of weights as the "memory" of a model — they encode the knowledge the model gains from its training data.
During training, a model processes text, learns from patterns and adjusts its weights to improve accuracy. Once the training is complete, these weights are saved. This way, anyone can load the pre-trained model and use it rather than starting from scratch. It is a huge time-saver and allows more people to use powerful models without the need for extensive computing resources.
What are Open Weight Models?
An open-weight model is one where the trained parameters (weights) are made publicly available. That means developers, researchers, and hobbyists can download and use them for their tasks.
Why Open Weights Matter:
- No Need to Retrain: Saves resources by skipping training.
- Quick Experimentation: Developers can test models easily.
- Supports Research: Enables fair comparison and reproducibility.
However, open-weight models don’t necessarily reveal everything. Often, the model architecture, training code, and dataset used are still kept private.
Examples of Open Weight Models:
- LLaMA 3 (Meta): Offers weights for public use, though under a restrictive license.
- Mistral 7B (Mistral AI): Released under an Apache 2.0 license, making it more accessible for commercial and research use.
What are Open Source Models?
Open-source models take the concept a step further. They not only provide access to the model weights but also share the architecture, training code, and often the training dataset.
This transparency allows anyone to:
- Modify the model’s design
- Retrain it on new data
- Understand how it works
Open-source models promote a collaborative ecosystem where the AI community can improve, debug, and build upon shared resources.
Examples of Open Source Models:
- BLOOM (BigScience): A multilingual model with fully open code, weights, and training details.
- GPT-2 (OpenAI): Provided both weights and code, inspiring widespread research.
- Falcon Models (TII): Released under Apache 2.0, with full model code and weights.
Key Differences Between Open Weights and Open Source
While the terms sound similar, their implications are quite different.
Feature | Open Weight Models | Open Source Models |
|---|---|---|
Access | Trained weights only | Weights, code, and often training data |
Transparency | Low to moderate | High — full model visibility |
Modifiability | Limited — can’t change architecture | Fully modifiable and retrainable |
Architecture Access | Often not shared or partially available | Fully shared |
Training Code | Not provided | Provided |
Training Data Info | Rarely disclosed | Often documented or included |
Community Role | Minimal | Strong community development and contributions |
Ease of Use | Easier for quick deployment | Requires more technical skill |
Licensing | Varies — may have usage restrictions | Typically permissive (Apache, MIT, etc.) |
Support | Limited to docs/forums | Active community support |
Cost | Free weights; compute costs apply | Free; infrastructure costs may apply |
Use Cases | Fast prototyping, inference, demos | Research, fine-tuning, academic projects, transparency needs |
Ethics & Fairness | Less visibility into training sources | Promotes ethical AI through openness |
Adding Closed Source Models to the Picture
Now that this post has covered open approaches, it’s worth understanding closed-source models, too. These models are completely proprietary.
Developers cannot:
- Access the weights
- Modify the model
- View how the model was trained
Instead, they use the model through an API or product interface. Examples include GPT-4, Claude, and Gemini Ultra. While these are easy to use and offer high-quality outputs, they lack transparency and control.
What It Means for Developers and Researchers
Each model type serves a different need:
- Open Weight Models are ideal for quick prototyping or deploying high-quality models without high infrastructure costs.
- Open Source Models are best for teams needing deep customization, educational purposes, or transparency.
- Closed Source Models suit businesses looking for plug-and-play solutions with reliable company support.
Also, responsible AI development is a key factor. Models that are open (especially open source) support ethical practices like fairness, transparency, and accountability. They allow the community to examine biases, data sources, and algorithmic behavior.
How to Use Open-Weight Models
Using open-weight models like Mistral 7B involves a few core steps:
- Install required libraries – typically includes AI model libraries and frameworks like Transformers and PyTorch.
- Load the tokenizer and model – you use the pre-trained weight files to load the model into memory.
- Prepare inference settings – set up text generation configurations (like temperature and token limits).
- Run the model – provide a prompt and generate a response.
If hardware is limited, models can be quantized (compressed) to run on less powerful systems using special configuration tools.
How to Use Open Source Models (Conceptual Workflow)
Let’s take GPT-2, a fully open-source model, as an example:
- Install transformer libraries if you're using a Python-based framework.
- Access the model and tokenizer through an open model hub or repository.
- Load and test — you can generate text, inspect the model’s layers, or even modify the architecture.
- Retrain or fine-tune — if needed, using your dataset for specialized tasks.
Since the source code is open, developers can go far beyond basic usage—like exploring how the model handles language or creating entirely new versions.
Conclusion
As the AI ecosystem grows, understanding open-weight and open-source models becomes crucial for developers and researchers. Open weights provide access to powerful models without the need for training, while open source models offer full transparency and control. Both are helping to democratize AI development—making it more accessible, ethical, and innovative.
Whether you're a hobbyist exploring ideas or a researcher building new architectures, there’s a model type for your needs. In a world increasingly driven by AI, knowing how models are shared is as important as what they can do.